原文链接:Borg: the Next Generation
一、主旨
Borg在2011年公开了当年五月的真实负载记录,并在2019年再次公开了当年五月的新一份真实负载记录。文章尝试分析对比两份真实数据,以窥Borg这些年的发展。
二、内容
略。
文章结构不重要,客观的数据对比可以再次精读,这里仅对有建设性的分析做摘取和总结。
三、关键点
1. 资源需求的极端多样以及资源占用的极端长尾分布
Borg集群中,不同任务对资源的需求是极端多样的,比世界上处理最多样化的计算任务的超算中心还要更多样1-2个数量级。
资源占用方面,1%的任务要占用超过99%的资源总量(CPU和内存皆如此),0.1%的任务都要占掉超过93%的资源总量,相较于普遍认知的80-20规律,有着更加极端的长尾效应。
其实这是符合常理的,当集群规模变得巨大,业务众多,任务量爆炸且各不相同,必然会带来资源需求的多样性;而集团资源必然向核心业务倾斜,一定会有极少量业务要拿走大部分资源,带来实际资源使用上的长尾效应。
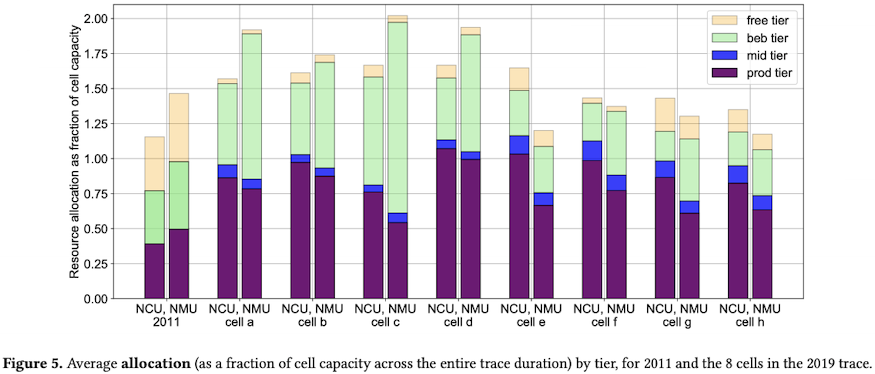
2. 超售比的提高带来整体的资源利用率上升
离线任务采用BE资源的情况显著增加,作为资源利用率提升的主要原因。
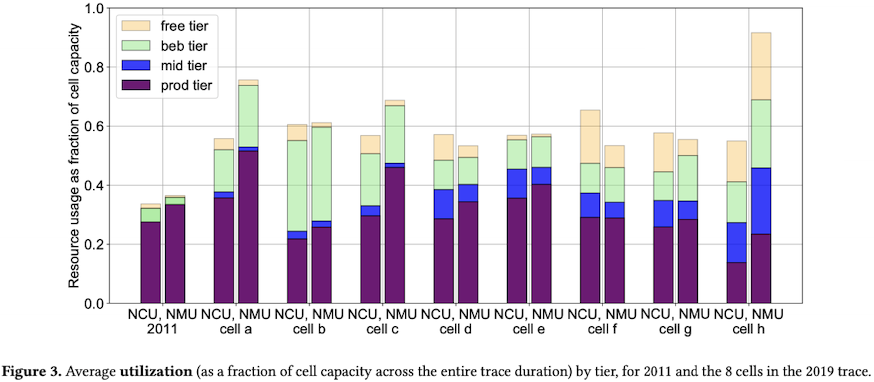
The average utilization has increased over 8 years, mostly due to an increase in consumption from the best-effort batch tier […]
CPU的超售比从2011年的1.25上升到2019年的1.5。
内存的超售在2011年几乎没有(Borg2015中将内存称为incompressible resource),但2019年也有了1.5的超售比。
鉴于2019年的数据涵盖了8个集群,在分集群视角上,有1个集群的内存超售比超过了2,另有2个集群的内存超售比接近2。
3. 痕迹数据/监控数据的采集
尽可能多地采到各方面的细节。
自动化地验证一些invariants,例如:实际占用的计算资源数量应小于集群的资源总量、一个任务的“提交”操作在时间维度上应当早于“结束”。文章指出,在实际采数据的时候往往会出现反直觉的数据表现,从而影响了数据本身的可信度,并且,自动化的验证流程应当尽早纳入数据采集的过程中。当这些反直觉现象出现时,应当研究其背后的原因并做出合理的解释。
Given the vagaries of large-scale trace data collection, we found that most of these invariants were violated occasionally. […]
Automated validation […] one-off scripts to a repeatable pipeline […] In retrosepct, we should have started with that […]
4. 可解释的调度是研究方向
两方面好处:(1)面向运维,可以明晰集群的整体运行状态;(2)面向用户,可以有指导性作用。
It would be nice to be able to provide explanations for why the scheduler made the decisions it made - either to help system operators understand what is going on (or is about to), or to provide guidance to end users on how they could better use the cluster.
四、引申
- Borg2019数据集:J. Wilkes. Google cluster-usage traces v3. Technical report at https: //github.com/google/cluster-data, Google, Mountain View, CA, USA, Nov. 2019.
- 阿里的数据集:Alibaba cluster data: using 270 GB of open source data to understand Alibaba data centers. Blog post, url = https://www.alibabacloud.com/blog/594340, Jan. 2019.
- Azure的数据集:Azure Public Dataset. https://github.com/Azure/AzurePublicDataset. Accesses 2020-03.
- Borg2011数据集的分析:E. Cortez, A. Bonde, A. Muzio, M. Russinovich, M. Fontoura, and R. Bianchini. Resource central: Understanding and predicting work- loads for improved resource management in large cloud platforms. In 26th Symposium on Operating Systems Principles (SOSP), pages 153–167, Shanghai, China, 2017. ACM.